Painting German tanks
To start your journey with painting German military vehicles of the Second World War you don’t Reed large palette of paints. At first, you need to decide which tank, armored car, car or truck you want to reconstruct. You can either focus on most accurate reconstruction of equipment from photography, illustration or description or try to create your own vision of the piece. You can restore living history, by making a small plastic model. No matter which way you’ll choose, most of the colours used by German Army would be the same.
After you decide which vehicle you’ll work with, you should check where and when did it serve. There are some vehicles, like Kübelwagen, Panzer III or Marders, which were used widely by Wehrmacht during the whole war. In that case, the choice of camouflage will be utmost. On the other hand, you won’t find King Tiger in Panzergrau, will you? For our guide, we will distinguish four periods of painting German vehicles: early, mid, late and for warfare used in the North African campaign.
Early type camo
At the start of the conflict, Germans used very simple patterns of camouflage. All vehicles were painted in gray Panzergrau color (RAL 7021). With experience gained on battlefields across the Europe, it became clear that additional camouflage would be necessary. At first, tank crews used... mud, to “paint irregular spots on the armor. Then, additional brown and green paints were used.

Tiger I in winter camo and in early production Panzergrau color.
Mid war camo
Through the war, the gray and extemporary proved itself to be insufficient. Especially on the eastern front, gray silhouettes of tanks were way too easy target for Soviet gun crews. In 1942, and officially in instructions from 1943, new base paint for German armor was used as base color. It was dark yellow Dunkelgelb (RAL 7028). Subsequently, the armour of tanks was painted with irregular spots, streaks and lines with two additional colors: dark green Olivegrün (RAL 6003) and dark brown Rotbraun (RAL8017). During spring-summer period camo colors were mostly green, during fall camo were more brownish. There were situations when the much-needed equipment was sent to first line units before painting the camouflage. In that case, the vehicle went to fight only painted only with the base, dark yellow color. pomalowany jedynie kolorem podstawowym.
There were also more complicated types of camouflage, using additional dark green and dark brown colors. Those camo patterns were called “Ambush” and “Splinter”. First one was a variation of spots camouflage. The difference were extra dots, or small spots painted on basic type camo, green and brown on yellow, brown and yellow on green and green and yellow on brown. The second one, the “Splinter” was easier to make, by painting regular stripes, or geometrical shapes with sharp edges.

Sturmtiger in “Ambush” type camo".

Rather unique “Splinter” type camo. Picture from tanks-encyclopedia.com, a very useful source of information about tanks and armored warfaremieckich czołgów.
During winter, camouflages described before weren’t much use, because of a snowy landscape. In those conditions, yellow, green and brown camo was an easy target for the enemy. Because of that white washable paint or calcium were used. It was common, that basic camouflage shined through the white paint. On most vehicles, all tank markings were left unpainted.
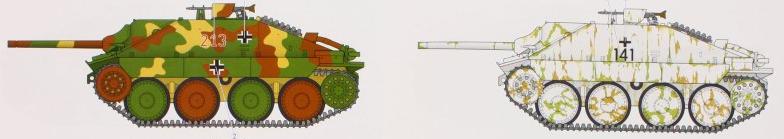
Hetzer in typical three color camouflage and in winter camouflage.
Late war camo
With the war coming to an end, the economical situation of Nazi Germany was becoming more and more hopeless. Shortages of supplies and allied bombers hit factories hard, so less and less equipment was resupplied for retreating Wehrmacht. Tanks which were provided to frontline units were sometimes unfinished or scrapped from few destroyed or damaged vehicles. Sometimes turret, hull, Schürzen, engine and other components were taken from another vehicle each. In that case, no one bothered to unify camouflage of salvaged tank.

Late version of Tiger I tank in yellow-brown camo.
In 1944 the painting of German tanks was obverted. Olivegrün became the basic color, while Dünkelgelb became camouflaging one. Another new method, designed to save time and resources, was painted dark green camouflage over anti-corrosion primer hull red (Rotbraun RAL 8012). Sometimes because of lack of either materials or time, some parts of the tank were left in base primer color. Because of that, some late war vehicles, especially those defending German mainland and Berlin, were often painted in very strange way.Nie będzie więc zdziwieniem że w obronie Berlina walczyły czołgi pomalowane w dość osobliwy sposób.
Africa
Main theatres of war in Africa, Tunisia and Libya, can be considered as desert countries, but their landscape is very differential. Beside sandy pathless tracts, you can spot oasis full of greens. Desert landscape also varied one from another. The difference was not only in flora but in types of rocks and sand. The only common thing in that unfriendly environment was that tanks painted in Panzergrey were easy targets.
Circumstances in which German units were transferred to Africa required haste, so very often equipment wasn’t prepared to landscape and conditions of the climate. First vehicles were simply painted in basic Panzergrey and were spontaneously camouflaged by their own crews with any masking paint they could lay their hands on. With the time spent in North Africa, camouflage patters evolved. The basic color for Africa Corps equipment was brown yellow (Gelbbraun, RAL 8000). The colour chosen for camouflaging was green gray (Grau Grün, RAL 7008).
By the time of German defeat on this theatre of war, painting of their vehicles changed. The basic colour was brown (Braun, RAL 8020), and camouflage was made with Feldgrau.wym, nieco ciemniejszym od poprzedniego (Braun; RAL 8020).
You need to remember that besides camouflage methods presented in our guide, sometimes vehicles varied. For example, Tigers from Schwere Panzer Abteilungs (heavy tank battalions) fought in Africa, and on all European fronts. Very often, one tank served on each of them. Older tanks, especially Panzers I and II were used in the militia and to fight resistance or partisans. There should be no wonder that we can spot a tank which camo is a hybrid of few camo and paint types (for example Gelb Brown basecoat and Olivegrün camouflage). The way you paint your tank will depend on two things: your own creativity and curiosity, to find more and more information about the reconstructed vehicle.
Below we present you a table with paint palette from most popular producers, which will help you choose colors for your German vehicles from World War II.
Firma/ Farba | Vallejo Model Color
| Vallejo Model Air | Vallejo Surface Primer | Tamiya Enamel Tamiya Acrylic
| Tamiya TS (spraye) | Humbrol | Revell | Pactra |
Panzergrau [RAL 7021] | German Grey (167) | German Grey
(52) | German Panzer Grey
(73.601) | German Grey (XF-63) | German Grey
(TS-4) | Matt Tank Grey (67) | Tank Grey, Mat (78) | Schwarzgrau (107) |
Dunkelgelb [RAL 7028] | DarkYellow
(116) | DarkYellow
(25) | German Dark Yellow
(73.604) | Dark Yellow (XF-60) | Dark Yellow
(TS-3) | Matt Middle Stone (225) | Sandy Yellow, Mat (16) | Panzer Dunkelgelb
(104) |
Rotbraun 1 [RAL 8017] | Hull Red
(146) | Armour Brown
(41) | - | Red Brown (XF-64) | Red Brown
(TS-1) | Brown
(186) | Rust, Mat (83) | Panzer Schokobraun
(105) |
Olive Grün [RAL 6003] | Retractive Green (90) | Medium Olive
(92) | - | Olive Green (XF-58) | Olive Drab 2
(TS-28) | Light Olive
(86) | Olive Green, Silk
(361) | Panzer Olive Grün (106) |
Rotbraun 2 [RAL 8012] | Burnt Red
(34) | Brown
(105) | German Red Brown
(73.605) | Hull Red
(XF-9) | Hull Red
(TS-33) | Matt German Cam. Red (160) | Reddish Brown, Mat (37) | Rot Braun
(103) |
Gelb Braun [RAL 8000] | Green Brown
(114) | Khaki Brown
(24) | German Green Brown
(73.606) | Desert Yellow (XF-59) | - | Matt Light Earth
(119) | Dark Earth, Mat (82) | Africa Yellow
(20) |
Braun
[RAL 8020] | Brown Sand
(132) | Camouflage Brown
(117) | - | Buff (XF-57) | Light Sand (TS-46) | Matt Desert Yellow (93) | Ochre Brown, Mat (88) | DAK Gelb Braun
(102) |
Grau Grün [RAL 7008]
| Green Grey
(101) | Grey Green
(116) |
- | Khaki Drab
(XF-51) | - | Khaki Drab
(159) | Olive Brown, Mat (86) | Field Drab, Mat (23) |
Colors were chosen are based on painted examples. Colors may vary depending on the producer, because of their individual pallets. Our choices are the most accurate and similar colours for painting German vehicles of World War II era. We recommend using paints from one manufacturer.
Colors we presented are necessary to paint basic color and camouflages. You need to remember that you’ll need additional colours for antennas, equipment, tracks and other parts. We recommend universal color such as gunmetal (for tracks, machine guns, metal parts of equipment), black (for tires and rubber elements) and brown (for wooden parts). Each of paint manufacturers has those in their basic palettes.
We hope you enjoyed our guide, please follow us for it’s more to come.
Author: Mikołaj Sułkowski
0
 EN
EN





